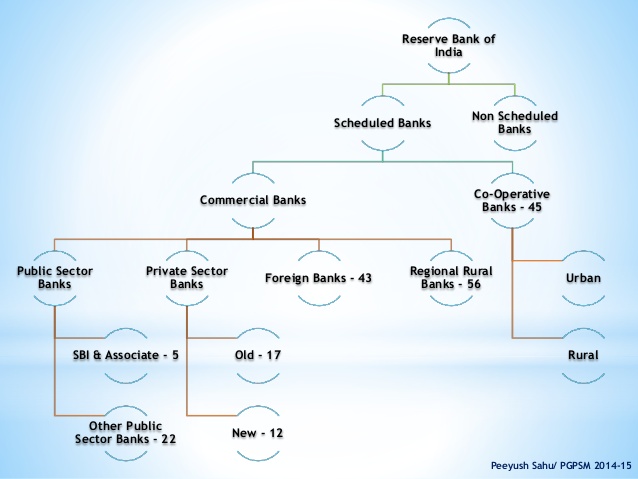
Scheduled & Non-Scheduled Bank
bankBanks implies the financial institution that takes public deposits and extends credit to those who need it. They are a substantial part of the financial system, which assists in the overall economic development. These are broadly classified as scheduled and non-scheduled banks in India regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, wherein scheduled banks include all the commercial banks like nationalized, foreign, development, cooperative and regional rural banks.
On the other extreme, non-scheduled banks are the banks that do not adhere to the norms prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). In this article excerpt, you can find out all the relevant differences between scheduled and non-scheduled banks in India.
Scheduled Versus Non-scheduled banks
A bank is called a scheduled bank in India, if it is listed in the second schedule of the RBI Act, 1934. In order to be included under this schedule of the RBI Act, banks have to fulfill certain statutory conditions such as:
- These banks need to have paid up capital and reserves of at least Rs. 0.5 million (50 Lakh)
- They should satisfy the CRAR norms and other prudential norms of RBI
- They should satisfy the RBI that their business is not being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of its depositors.
In our country all banks are scheduled banks except four Local Area Banks and some Non-scheduled Urban Cooperative Banks. As of February 2015, these four local area banks are:
- Coastal Local Area Bank Ltd – Vijayawada (Andhra Pradesh)
- Capital Local Area Bank Ltd – Phagwara (Punjab)
- Krishna Bhima Samruddhi Local Area Bank Ltd, Mahbubnagar (Andhra Pradesh)
- Subhadra Local Area Bank Ltd., Kolhapur (Maharashtra)
The scheduled banks are further classified into Scheduled Commercial Banks and Scheduled Cooperative Banks. The basic difference between scheduled commercial banks and scheduled cooperative banks is in their holding pattern. Scheduled cooperative banks are cooperative credit institutions that are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act. These banks work according to the cooperative principles of mutual assistance.
List of Scheduled Banks in India
Scheduled Commercial Banks can be divided as follows:
1. Scheduled Commercial Public Sector Banks:
Public Sector Banks (PSBs) are banks in which the government has a majority stake that is more than 50%. The shares of public sector banks are listed on stock exchanges.
As of now, India has 27 Public Sector Banks. This number includes SBI, its 5 associates and 19 other nationalized banks. Two other banks, namely IDBI and Bhartiya Mahila Bank are two banks which have been categorized by RBI as “Other Public Sector Banks”.
- Andhra Bank
- Allahabad Bank
- Bank of Baroda
- Bank of India
- Bank of Maharashtra
- Canara Bank
- Central Bank of India
- Corporation Bank
- Dena Bank
- Indian Overseas Bank
- Indian Bank
- Oriental Bank of Commerce
- Punjab National Bank
- Punjab and Sind Bank
- Syndicate Bank
- Union Bank of India
- United Bank of India
- UCO Bank
- Vijaya Bank
-
SBI and its associates:
State Bank of India (SBI) is India’s largest bank by assets. It has around 17,000 branches and around 200 foreign offices. It is the banker to millions of Indians and has over 2 Lakh employees. SBI was formed in the British Era. It is the child of three presidency banks, namely, Bank of Calcutta (which was later renamed as Bank of Bengal), Bank of Bombay and the Bank of Madras. In 1921, these three presidency banks were merged and the entity was called as the Imperial Bank of India. After about 35 years, in 1955, the Imperial Bank of India was nationalized and renamed as the State Bank of India. This makes SBI the oldest Bank in India.
In 1959, SBI had 8 associate banks. Currently, it has 5 associate banks. They are:
- State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur
- State Bank of Hyderabad
- State Bank of Mysore
- State Bank of Patiala
- State Bank of Travancore
In addition to the above, SBI also has 7 non-banking subsidiaries. They are SBI Capital Markets Ltd., SBI Funds Management Pvt. Ltd., SBI Factors & Commercial Services Pvt. Ltd, SBI Cards & Payments Services Pvt. Ltd. (SBICPSL), SBI DFHI Ltd, SBI Life Insurance Company Limited and SBI General Insurance.
Although SBI comes under the definition of a nationalized bank, RBI puts State Bank of India and its 5 associate banks under a separate category ‘SBI & Associates’).
2. Scheduled Commercial Private Sector Banks:
Private sector banks are those whose majority stake is in private hands. Indian has two types of private sector banks:
- Old Private Sector Banks
- New Private Sector Banks.
3. Old Private Banks:
There are 12 old private sector banks:
- Catholic Syrian Bank
- City Union Bank
- Dhanlaxmi Bank
- Federal Bank
- Jammu and Kashmir Bank
- Karnataka Bank
- Karur Vysya Bank
- Lakshmi Vilas Bank
- Nainital Bank
- Ratnakar Bank
- South Indian Bank
- Tamilnad Mercantile Bank
Of the above banks, Nainital Bank is a subsidiary of the Bank of Baroda. 98.57% stake in Nainital Bank is held by Bank of Baroda. There were also other old private sector banks which have now merged with other banks. For instance:
- In 2007 Lord Krishna Bank merged with Centurion Bank of Punjab.
- In 2006, Sangli Bank merged with ICICI Bank.
- In 2008, Centurion Bank of Punjab merged with HDFC.
2. New Private Sector Banks:
In 1993, RBI issued revised guidelines regarding the entry of private sector banks. Therefore, new private sector banks are the ones which were incorporated as per such revised guidelines. Currently, there are 7 new private sector banks:
- Axis Bank Limited
- Bandhan Bank Limited
- DCB Bank Limited
- HDFC Bank Limited
- ICICI Bank Limited
- IndusInd Bank Limited
- IDFC Bank Limited
- Kotak Mahindra ING Vysya Bank
- YES Bank Limited
3. Scheduled Foreign Banks in India:
As of now, there are 45 foreign banks which are operating as branches in India.
- Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Ltd.
- National Australia Bank
- Westpac Banking Corporation
- Bank of Bahrain & Kuwait BSC
- AB Bank Ltd.
- Sonali Bank Ltd.
- Bank of Nova Scotia
- Industrial & Commercial Bank of China Ltd.
- BNP Paribas
- Credit Agricole Corporate & Investment Bank
- Societe Generale
- Deutsche Bank
- HSBC Ltd.
- PT Bank Maybank Indonesia TBK
- Mizuho Bank Ltd.
- Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation
- The Bank of Tokyo- Mitsubishi UFJ, Ltd.
- SBM Bank (Mauritius) Ltd.
- Cooperatieve Rabobank U.A.
- Doha Bank
- Qatar National Bank
- JSC VTB Bank
- Sberbank
- DBS Bank Ltd.
- United Overseas Bank Ltd.
- FirstRand Bank Ltd.
- Shinhan Bank
- Woori Bank
- KEB Hana Bank
- Industrial Bank of Korea
- Bank of Ceylon
- Credit Suisse A.G
- CTBC Bank Co., Ltd.
- Krung Thai Bank Public Co. Ltd.
- Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank Ltd.
- Mashreq Bank PSC
- First Abu Dhabi Bank PJSC
- Emirates Bank NBD
- Barclays Bank Plc.
- Standard Chartered Bank
- The Royal Bank of Scotland plc
- American Express Banking Corporation
- Bank of America
- Citibank N.A.
- J.P. Morgan Chase Bank N.A.
There are 5 Non-Scheduled Urban Cooperative Banks in India
1 Akhand Anand Co-Operative Bank Ltd
2 Alavi Co-Op Bank Ltd
3 Amarnath Co-operative Bank Ltd
4 Amod Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd
5 Amreli Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd
Along with this 4 local area banks in India which, forms under non-scheduled list of Banking as per RBI.
1. Coastal Local Area Bank Ltd
2. Capital Local Area Bank Ltd
3. Krishna Bhima Samruddhi Local Area Bank Ltd
4. Subhadra Local Area Bank Ltd












