Molar Volume
The volume occupied by one mole of any substance in the gaseous state at a given temperature and pressure is called molar volume.
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance (chemical element or chemical compound) at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass (M) divided by the mass density (ρ). It has the SI unit cubic metres per mole (m3/mol),although it is more practical to use the units cubic decimetres per mole (dm3/mol) for gases and cubic centimetres per mole (cm3/mol) for liquids and solids.
Molar Volume formula
The Molar volume is directly proportional to molar mass and inversely proportional to density. The formula of molar volume is expressed as :
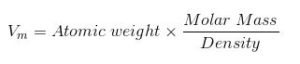
Where Vm is the volume of the substance.
Example :-
The decomposition of NaClO3 produces NaCl and O2. Determine the volume of O2 if 42.6 g NaClO3 decomposes at STP? The density is given to be 0.213g/m3.
Solution :-
Parameters given are,
Density(ρ) = 0.215kg/m3
Molar mass = 42.5g/mol = 0.0425kg/mol
Atomic weight = 96
To substitute in the equation
Vm = Atomic weight x Molar mass / Density
= 96 x 0.0425 / 0.215
Therefore, Vm = 18.976 m3/m











