General Tips for Tenses in English Grammar
A verb’s tense indicates the time interval during which an event or an action has occurred. Tenses form a major part of our spoken as well as written English and plays an important role in understanding conversational English. Many times, we end up making silly mistakes related to tenses. Here are a few general rules of tenses.
There are three major tenses and theses are further subdivided. They are:
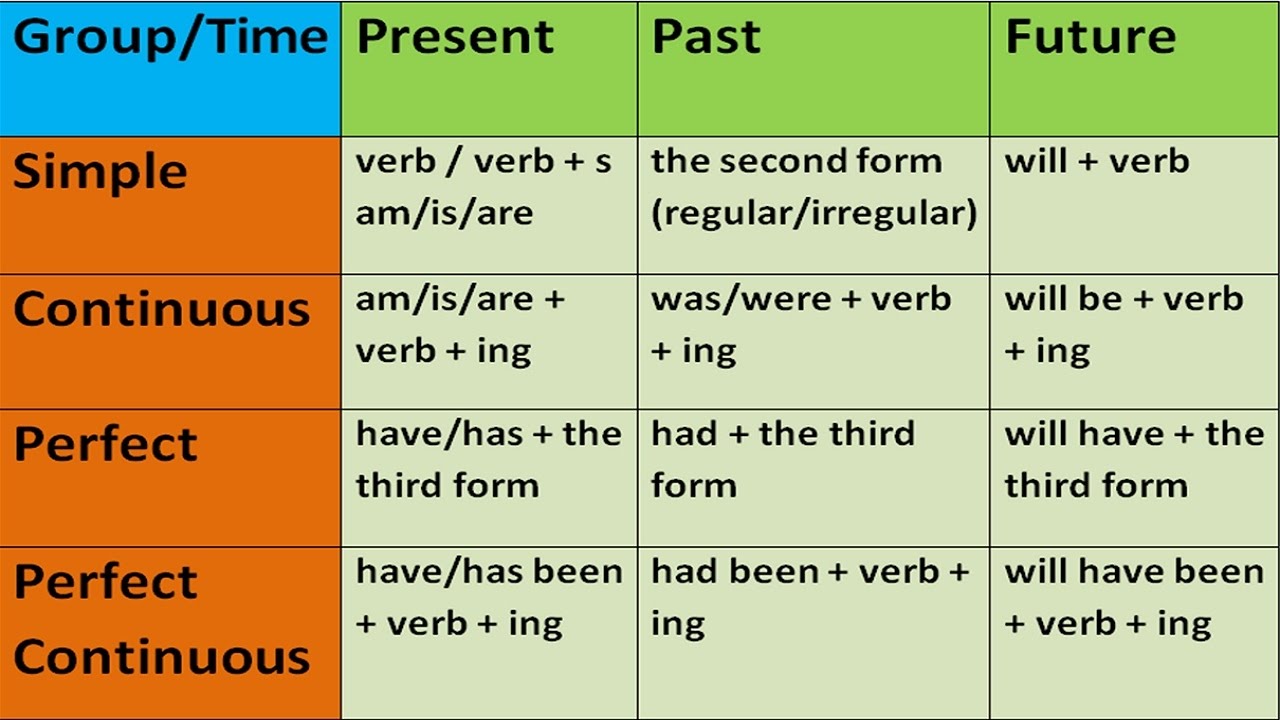
1. Past
- Simple past (Verb+ed)
This tense is used to indicate a habitual action or a single act that has happened in the past. Past participle of the root verb is used in this tense, which is formed by adding ‘ed’ to the end of the root verb.
E.g.: Sachin scored a century in the last match.
E.g.: He studied many hours a day.
However there are certain exceptions to the rule of forming past tenses by adding ed to the verb. These have irregular past participle forms.
E.g.: Blew, came, drove
- Past perfect (Had/Have+Past participle):
This tense denotes an action which has been completed in the past before the occurence of another action. Action described by this tense is definitely ended in the past. This generally compares two actions that have taken place in two different time periods.
E.g.: I had completed my assignment way before its deadline (arrived).
E.g.: The rain had stopped when we came out.
- Past continuous (Was/Were+Present Participle):
This tense describes an action that was ongoing for some time in the past. It is generally used to describe an action which was ongoing when an another action took place around the same time.
E.g.: I was playing the guitar when Lakshmi walked into my room.
- Past perfect continuous (Had/Have been+Present participle):
This tense indicates an action that began at a particular point of time in the past and contiued for a certain amount of time up to a particular moment in the past.
E.g.: I had been practising Mathematics since ten in the morning.
2. Present
- Simple present (Verb+s/es):
This tense describes universal truths, regular actions and habits which occur daily or at particular intervals of times.
E.g.: The Sun rises in the East.
- Present perfect (Has/have+Past participle):
This tense indicates an action that has just been completed, usually used to denote an action that began in the past but continued until the present moment.
E.g.: He has solved the sum.
E.g.: We have lived here for ten years.
- Present continuous (Am/is/are+Present participle):
This tense describes an action which is currently happening and will continue to happen for a short amount of time or may be for a long amount of time.
E.g.; The girls are getting ready for their performance.
- Present perfect continuous (Has/have+been+Present participle):
This describes an action that began at a particular point of time in the past and has continued to progress until now.
E.g.: I have been studying for my examinations for over a month.
3. Future
- Simple future (Will+Verb/Am/is/are+going to+verb):
This tense describes an action that is going to happen in the future.
E.g.: Reeta is going to visit her relatives next month.
E.g.: I will call him tomorrow.
- Future perfect (Will have+Past participle):
This is used to compares two actions and describes an action that will take place before something else in the future.
E.g.: By tomorrow evening, I will have completed my project.
- Future continuous (Will be+Present participle):
This is used to describe a continuous action in the future or two actions that will be occurring simultaneously in the future.
E.g.: Next year I will be applying for entrance to colleges.
E.g.: Tomorrow, I will be going to the university to get my certificates.
- Future perfect continuous (Will have been+Present participle):
This tense is hardly used in our practical life. It is used either to show a period of time before something will occur in the future or to establish a cause and effect relationship.
E.g. Derek will be exhausted by the time he makes his million because he will have been managing two companies by himself for over three years.
In each case above, the same rule applies to each sub-type, whether the sentence be affirmative, negative or interrogative. Examples-
- Sheila goes for a jog daily. (Affirmative)
- Sheila does not go for a jog daily. (Negative)
- Does Sheila go for a jog daily? (Interrogative)
For a general sentence, this is how the conversion will take place:
- Yash ate an ice-cream yesterday. (Simple past)
- Yash had eaten an ice-cream the day before. (Past perfect)
- Yash was eating an ice-cream an hour ago. (Past continuous)
- Yash had been eating an ice-cream before going to class. (Past perfect continuous)
- Yash eats an ice-cream every other day. (Simple present)
- Yash has eaten an ice-cream. (Present perfect)
- Yash is eating an ice-cream now. (Present continuous)
- Yash has been eating an ice-cream for the past half an hour. (Present perfect continuous)
- Yash will eat an ice-cream after dinner. (Simple future)
- Yash will have eaten an ice-cream by the time you come. (Future perfect)
- Yash will be eating an ice-cream when you come. (Future continuous)
- Yash will have been eating an ice-cream by the time you come. (Future perfect continuous)
| Maths Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download | English Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
| GK/GS/GA Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download | Reasoning Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
| Banking Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download | DI Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
| All Subject Topicwise Short Tricks > Click Here To Download | Static GK & Awareness Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
| Please Support us by Joining Below Groups & Like Our Pages we will be very thankful to you. | |
| Facebook Page : https://www.facebook.com/governmentadda/ | |
| Facebook Group : https://www.facebook.com/groups/governmentadda/ | |
| Telegram | Official Channel : https://telegram.me/GovtAdda |
| Current Affairs Channel : https://telegram.me/Ga_Buzz | |
| UPSC Channel : https://telegram.me/CivilServicesAdda | |
| SSC Channel : https://telegram.me/SscAdda | |
| Banking Channel : https://telegram.me/IbpsZone | |
| RBI Group : https://telegram.me/RbiZone | |
| Railway RRB Channel : https://telegram.me/RailwayZone | |
| IT Officer Group : https://telegram.me/IT_Officer | |
| Insurance Group : https://telegram.me/InsuranceZone | |
| Job Alert Channel : https://telegram.me/JobAlert | |
| https://twitter.com/GovtAdda | |
| https://www.instagram.com/governmentadda/ | |
| https://www.pinterest.com/governmentadda/ | |
| Youtube | Click Here To Subscribe Now |
Thanks,
Team GovernmentAdda
Share & Support Us









